Among Black, Hispanic and multiracial mothers, 40 percent said they had been mistreated during pregnancy or childbirth.
The News
One in five women in the United States said they had been mistreated while receiving maternity care, and almost one in three said they had experienced discrimination because of factors like age, weight or income, according to a survey of 2,400 mothers released Tuesday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Women of color reported even higher rates. Roughly 30 percent of Black, Hispanic and multiracial women said they had been mistreated, and 40 percent of Black and multiracial women reported discrimination because of race and ethnicity, income, type of health insurance or differences of opinion with caregivers, among other reasons.
Among the most common complaints about mistreatment: health care providers ignoring their patients, refusing requests for help or failing to respond to a call for help in a timely manner. Women reported being shouted at or scolded, having their physical privacy violated and having health care providers threaten to withhold treatment or force them to accept medical interventions they did not want.
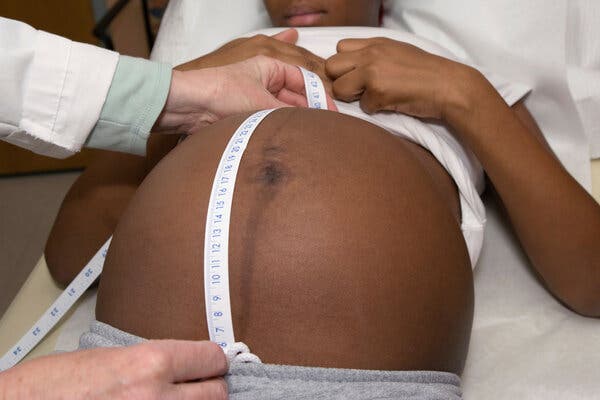
Why It Matters: Many pregnant women are afraid to discuss their worries.
Almost half of the women surveyed said they had held back in talking with a maternity care provider about their questions or concerns, a particularly disturbing finding. The most common reason given was that patients thought that what they were experiencing was normal.
Other common reasons: Women said they didn’t want to “make a big deal” about a problem, or were embarrassed to talk about it; they’d been told by friends or family that the problem was “a normal part of pregnancy”; or they feared being seen as a difficult patient.
Some also said they held back because their provider seemed to be in a rush, and they weren’t sure their concern was important enough to merit additional attention, or they were scared to talk about it.
Background: Maternal mortality rates have soared in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the United States are among the highest in the industrialized world. They have risen steadily in recent years, with a sharp but apparently temporary spike during the pandemic.
Black and Native American women are at particularly high risk. Maternal mortality rates are two to three times higher among these women than among white and Hispanic women.
Yet studies have found that the vast majority of the deaths — some 80 percent — are preventable.
The new survey, which was designed by the C.D.C. and carried out by the communications consultancy firm Porter Novelli, included some 2,400 mothers of children ages 5 or older, who answered questions online between April 24 and April 30 of this year.
The survey was not a nationally representative sample of the population giving birth, however, so its utility is somewhat limited. Nevertheless, the findings suggest serious flaws in the care provided to pregnant women and women giving birth.
A First Step: Hearing the patient.
Birthing women deserve respectful health care, which is strongly linked to positive outcomes, C.D.C. officials said.
“If you are consistently feeling like your concerns are not being heard and you’re experiencing mistreatment, you’re less likely to seek further treatment in the future,” said Dr. Wanda Barfield, director of the agency’s division of reproductive health.
“And for those women who may be at higher risk and have a concern that may be life-threatening — if they are reluctant to seek help, and this study suggests that almost half of them are, they may be at risk for a very adverse outcome.”